Introduction to Injection Molding Stages
Injection molding, a pivotal process in manufacturing, transforms raw plastic into intricate parts through a series of precise stages. Each stage in this process plays a critical role in ensuring the final product meets quality and design specifications. From securing the mold to the intricate dance of injecting, cooling, and ejecting the material, understanding these stages is key to mastering the art of injection molding. This process not only demands technical expertise but also a deep understanding of material behavior under different conditions. And remember, for the best injection molding company Illinois has to offer, JDI Plastics is standing by!
Key Takeaways
- 4 Steps: Clamping, Injection, Cooling, and Ejection
- Precision: Each stage of injection molding requires meticulous control.
- Efficiency: Proper execution of each stage ensures high production efficiency.
- Quality: The quality of the final product hinges on the precision of each stage.
- Speed: Timely execution of stages contributes to overall production speed.
- Adaptability: Different materials may require adjustments in each stage.
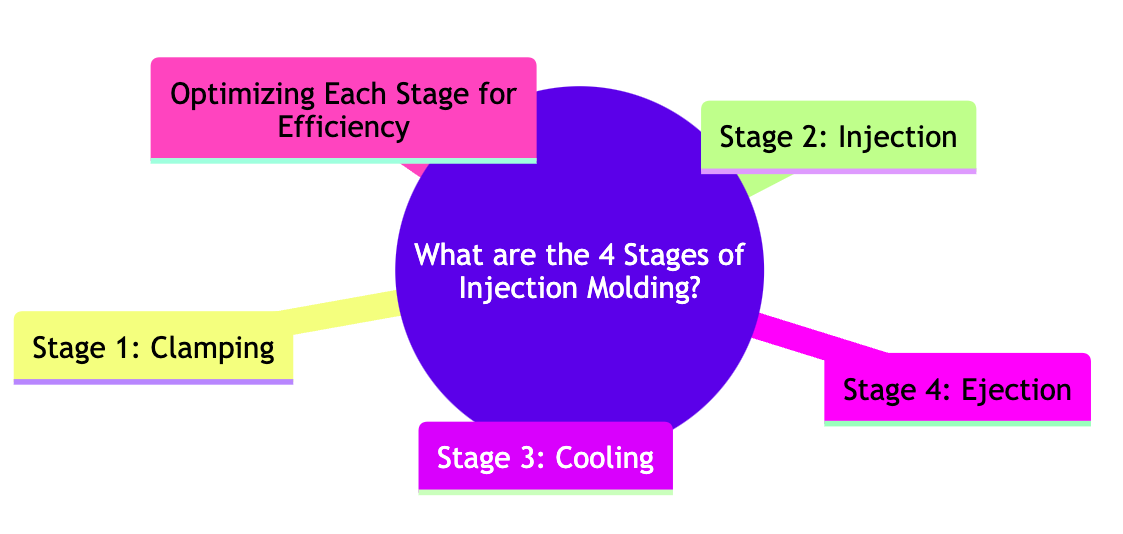
Stage 1: Clamping
The clamping stage is where the journey of injection molding begins. It's all about preparing the mold and securing it for the injection process. In this stage, the two halves of the mold are brought together and clamped with significant force. This is crucial to prevent any material from escaping during injection, ensuring the mold is filled precisely and consistently. The clamping force must be strong enough to withstand the pressure of the injected material but also calibrated to avoid damage to the mold.
Aspects of the Clamping Stage
- Mold Closure: Ensuring the mold closes correctly and aligns perfectly.
- Clamping Force: Apply sufficient force to keep the mold securely closed.
- Mold Stability: Maintaining mold stability to prevent defects in the final product.
- Safety Checks: Ensuring all safety measures are in place before proceeding.
- Preparation Speed: Balancing speed and precision in mold preparation.
Stage 2: Injection
The injection stage is where the actual molding takes shape. Here, the pre-melted plastic material is injected into the closed mold at high pressure. This stage is critical as it determines the quality of the internal structure and surface of the final product. The injection is done through a heated barrel equipped with a reciprocating screw, ensuring the material is evenly distributed within the mold. The pressure and speed of injection are finely tuned to match the material's properties and the mold's design, ensuring flawless filling without defects.
Comparison of Injection Parameters for Different Materials
|
Material |
Injection Pressure |
Injection Time |
|
ABS |
Medium-High |
Moderate |
|
Polyethylene |
Low-Medium |
Short |
|
Polycarbonate |
High |
Long |
|
Nylon |
Medium |
Moderate |
|
PMMA |
Medium-High |
Moderate-Long |
Stage 3: Cooling
Once the mold is filled, the cooling stage begins. This is where the molten plastic starts to solidify into the shape of the mold. The duration of the cooling stage is crucial as it directly impacts the cycle time and the quality of the product. If the cooling is too rapid, it can lead to warping or internal stresses in the part. Conversely, too slow cooling can increase cycle times and reduce production efficiency. Factors like the thickness of the part, the type of plastic used, and the mold design all play a role in determining the optimal cooling time.
Factors Influencing Cooling Duration
- Material Properties: Different plastics have varying cooling rates.
- Mold Temperature: The temperature of the mold needs to be controlled precisely.
- Part Thickness: Thicker parts require longer cooling times.
- Mold Design: Complex designs may need strategic cooling channels.
- Ambient Temperature: The surrounding environment can affect cooling efficiency.
Stage 4: Ejection
The ejection stage marks the completion of the molding cycle, where the solidified part is removed from the mold. This stage is as crucial as the others, as improper ejection can damage the part or affect its quality. The mold opens, and an ejection mechanism, typically a series of pins or a plate, gently pushes the part out of the mold cavity. The design of the ejection system is critical to ensure that the force is evenly distributed across the part to avoid warping or surface blemishes.
- Ejector Pins: Commonly used to push the part out from one side.
- Stripper Plates: Helpful for parts with undercuts or when a smooth ejection is needed.
- Air Blasts: Used to release the part using compressed air, ideal for delicate parts.
- Robotic Removal: Ensures precision and is ideal for complex or large parts.
Optimizing Each Stage for Efficiency
Maximizing efficiency in injection molding involves fine-tuning each stage of the process. This optimization leads to higher-quality products, reduced cycle times, and overall cost savings. Key areas to focus on include mold design, material selection, and process control.
- Streamline Mold Design: Simplify designs to reduce cycle times.
- Material Selection: Choose materials that suit the product requirements and mold efficiently.
- Process Control: Monitor and adjust parameters like temperature and pressure for optimal performance.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep machinery and molds in top condition to prevent downtime.
- Employee Training: Ensure staff are knowledgeable about best practices and efficiency techniques.
Conclusion: The Art and Science of Injection Molding
Understanding the four stages of injection molding – clamping, injection, cooling, and ejection – is essential for anyone in the field of manufacturing. Each stage plays a pivotal role in determining the quality and efficiency of the final product. JDI Plastics combines the art of precision engineering with the science of material behavior to master these stages, ensuring high-quality production. Their expertise in optimizing each stage for maximum efficiency sets them apart in the industry, making them a leader in injection molding. With a deep understanding of this process, JDI Plastics continues to innovate and excel, delivering exceptional results in every project.